Ultimate Guide To Databricks
If you’re dealing with any serious amount of data, whether you’re building machine learning models, running analytics at scale, or just trying to make sense of the chaos that is your company’s data infrastructure, you need to understand what Databricks brings to the table.
So let’s break it down.
What Is Databricks

The simplest way to think about Databricks is this: it’s a unified analytics platform that sits on top of your data lake and makes everything work together.
Built on Apache Spark (we’ll get to that in a second), Databricks was created by the original developers of Spark who looked at the ecosystem and thought, “We can make this so much better.”
And they did.
At its core, Databricks combines data engineering, data science, and business analytics into one collaborative workspace. Think of it as the Swiss Army knife of big data platforms, except instead of a tiny scissor and a toothpick, you get notebook environments, automated cluster management, and production-grade machine learning capabilities.
The platform runs on major cloud providers, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. This means you’re not locked into some proprietary infrastructure that’ll haunt you later when you need to migrate.
The Apache Spark Foundation
 Here’s where things get a bit technical, but stick with me because this matters.
Here’s where things get a bit technical, but stick with me because this matters.
Apache Spark is an open-source distributed computing framework. In plain English, it’s software that lets you process massive amounts of data across multiple computers at the same time. Really fast. Like, 100 times faster than traditional Hadoop MapReduce for certain applications.
Spark handles both batch processing (think: analyzing yesterday’s sales data) and stream processing (think: analyzing sales data as it happens right now). It’s versatile, powerful, and, let’s be real, sometimes a pain to set up and manage on your own.
That’s where Databricks comes in. The platform takes Spark and wraps it in a user-friendly interface with automatic scaling, optimized performance, and collaborative features that actually make sense. You get all the power of Spark without spending weeks wrestling with cluster configurations and dependency management.
The Architecture: How Databricks Actually Works
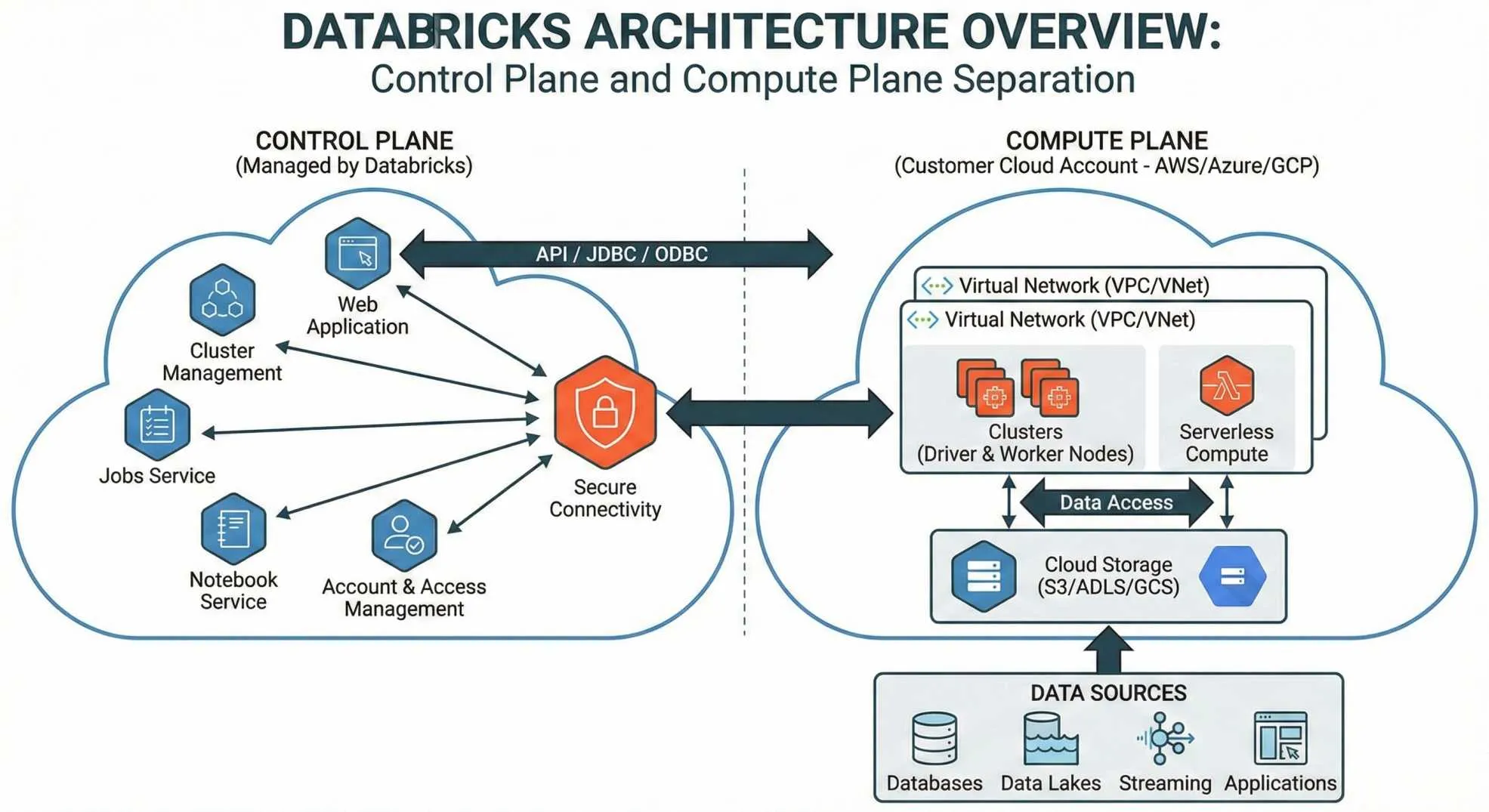 Databricks uses what they call a “lakehouse” architecture.
Databricks uses what they call a “lakehouse” architecture.
Traditional data architectures force you to choose between data warehouses (great for structured data and SQL queries) and data lakes (great for storing everything including the kitchen sink). The lakehouse architecture combines both approaches. You get the flexibility and scale of a data lake with the performance and ACID transactions of a data warehouse.
The platform has two main components:
The Control Plane
This manages your notebooks, cluster configurations, jobs, and security. This lives in Databricks’ own cloud infrastructure, which means they handle the maintenance and updates.
The Data Plane
This is where your actual data processing happens. This runs in your cloud account, AWS, Azure, or GCP, which means your data never leaves your control. Privacy-conscious companies love this setup because you’re not shipping sensitive data off to some third-party server.
When you spin up a cluster, Databricks creates a group of virtual machines in your cloud account. You can configure these clusters to auto-scale based on workload, which is fantastic for cost optimization. Why pay for 50 machines when you only need 5 right now?
Delta Lake
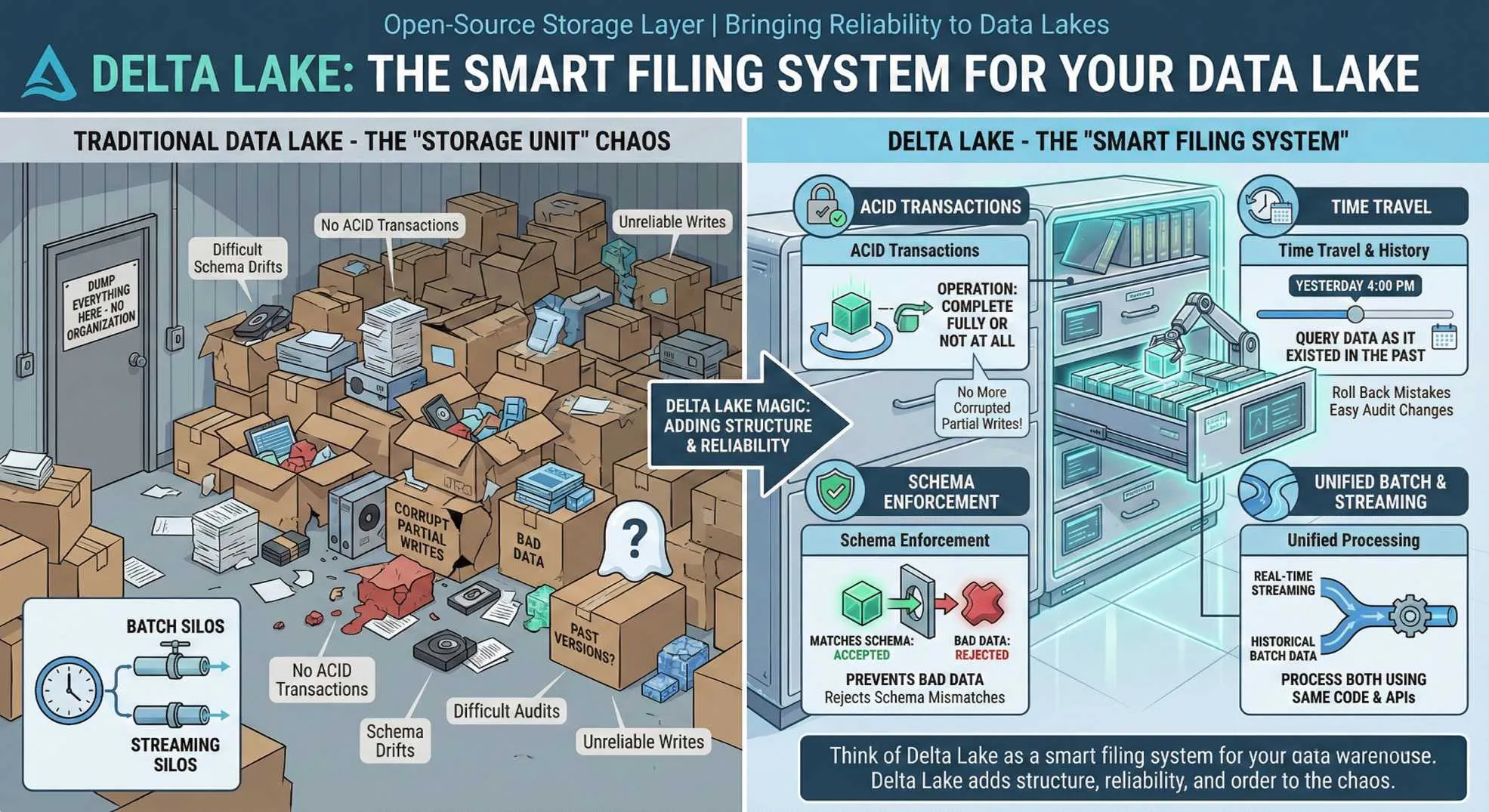 Let me tell you about Delta Lake, because this is where Databricks really shines.
Let me tell you about Delta Lake, because this is where Databricks really shines.
Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer that brings reliability to data lakes. Remember how I mentioned ACID transactions earlier? That’s Delta Lake doing its magic. It adds features like:
- ACID transactions: Your data operations either complete fully or not at all. No more corrupted partial writes.
- Time travel: You can query your data as it existed at any point in the past. Made a mistake? Roll back. Need to audit changes? Easy.
- Schema enforcement: Prevents bad data from corrupting your lake. If someone tries to write data that doesn’t match your schema, Delta Lake rejects it.
- Unified batch and streaming: Process real-time and historical data using the same code and APIs.
Think of Delta Lake as a smart filing system for your data warehouse. Traditional data lakes are like dumping everything into a massive storage unit with no organization. Delta Lake adds structure, reliability, and order to that chaos.
Think of Delta Lake as a smart filing system for your data warehouse.
Getting started: Your First Databricks Workspace
Alright, enough theory. Let’s talk about actually using this thing.
When you first log into Databricks, you’ll see a workspace, basically a web-based IDE where everything happens. The interface is clean, and you’ll spend most of your time in notebooks.
Databricks notebooks are similar to Jupyter notebooks if you’ve used those. You write code in cells, execute them, and see results immediately. But Databricks notebooks have some killer features:
-
Multi-language support: Mix Python, SQL, Scala, and R in the same notebook. Yes, really. You can write a SQL query in one cell and process the results with Python in the next cell.
-
Real-time collaboration: Multiple people can edit the same notebook simultaneously, Google Docs style. Comments, version history, the works. This is huge for teams.
-
Built-in visualizations: Run a query and Databricks automatically gives you visualization options. Bar charts, line graphs, maps, all without importing matplotlib or fighting with ggplot.
Creating your first cluster is straightforward. You pick your cloud provider, choose your machine types (go with something modest to start, you can always scale up), and decide whether you want the cluster to auto-terminate after a period of inactivity.
Pro tip: turn on auto-termination.
Data Engineering Workflows
Data engineering in Databricks revolves around creating reliable, reproducible pipelines that transform raw data into something actually useful. The platform provides several approaches:
-
Databricks Jobs let you schedule notebooks or Python/JAR files to run on a regular basis. Need to process yesterday’s data every morning at 6 AM? Create a job. The scheduler is robust, dependencies are straightforward, and monitoring is built-in.
-
Delta Live Tables (DLT) takes this further. Instead of writing procedural code to transform data, you declare what your data should look like, and DLT handles the execution. It automatically manages infrastructure, handles errors, and monitors data quality. It’s like having a really competent assistant who never needs coffee breaks.
The workflow usually looks something like this:
- Ingest raw data into your bronze layer (unprocessed, just stored)
- Clean and standardize into your silver layer (validated, deduplicated)
- Create business-level aggregates in your gold layer (analytics-ready)
This medallion architecture has become the de facto standard because it balances flexibility with governance. Raw data stays accessible for reprocessing, while cleaned data is ready for immediate use.
Machine Learning: From Experiment to Production
Let’s talk about MLflow, because this is where Databricks becomes indispensable for data science teams.
Machine learning is notoriously messy. You try dozens of models, tweak hyperparameters, test different features, and somewhere in the chaos, you lose track of what actually worked. Then, months later, someone asks, “What model did we deploy?” and everyone just shrugs.
MLflow solves this. It’s an open-source platform for managing the ML lifecycle, and it’s deeply integrated into Databricks.
Experiment tracking
Every time you train a model, MLflow logs parameters, metrics, and artifacts. You can compare runs side-by-side and see exactly which configuration produced the best results.
Model registry
Once you’ve trained something you like, register it. The registry tracks versions, stages (staging vs. production), and transitions. Need to roll back because your new model is performing worse? One click.
Model serving
Databricks can deploy your models as REST APIs automatically. No need to containerize, set up Kubernetes, or worry about scaling. It just works.
The integrated environment means you can train a model in a notebook, tune it with AutoML (yes, Databricks has automated machine learning), register it, and deploy it, all without leaving the platform. For teams trying to reduce their time-to-production, this is game-changing.
Databricks has automated machine learning.
SQL Analytics: Making Data Accessible to Everyone
Not everyone on your team can write Python.
Databricks SQL (formerly SQL Analytics) provides a query editor and dashboard builder for people who just want to ask questions of their data without learning Spark APIs. The interface feels familiar if you’ve used any modern BI tool, think Tableau or Looker, but running on your data lake.
You write SQL queries against Delta tables, create visualizations, and build dashboards. The queries run on serverless SQL warehouses, which means you don’t have to provision or manage clusters. Just run your query and get results.
The performance is impressive too. Photon, Databricks’ native query engine, accelerates SQL queries significantly. We’re talking 3-5x faster than standard Spark SQL for many workloads. When you’re running complex aggregations over billions of rows, that matters.
Unity Catalog
Unity Catalog provides centralized governance across all your Databricks workspaces. You define access controls in one place, and they apply everywhere. No more “wait, does the marketing team have access to customer PII?” panic moments.
The key features:
-
Fine-grained access control: Grant permissions at the catalog, schema, table, row, or even column level. Someone needs to see aggregate sales data but not individual customer names? Easy.
-
Automated lineage tracking: Unity Catalog tracks where data comes from and where it goes. You can see the full lineage from raw ingestion through transformations to final consumption. This is crucial for compliance and debugging.
-
Data discovery: Search for datasets across your organization. Metadata, descriptions, and ownership information are all indexed and searchable.
-
Audit logging: Every data access and modification is logged. When auditors come knocking (and they will), you have receipts.
For companies dealing with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2, Unity Catalog isn’t optional, it’s essential.
Cost Optimization
Here’s something nobody tells you when you’re first getting excited about Databricks: the costs can spiral if you’re not careful. Cloud compute is expensive, and Databricks adds its own layer of fees on top of your cloud provider’s charges.
But there are strategies to keep costs reasonable:
Right-size your clusters
Don’t use memory-optimized instances for CPU-bound workloads. Don’t use GPU instances unless you’re actually training neural networks. Match your hardware to your workload.
Use spot instances
For non-critical workloads, spot/preemptible instances can save 60-80% on compute costs. Yes, they can be interrupted, but Databricks handles restarts automatically.
Enable auto-scaling
Why pay for 10 workers when your job only needs 3 right now? Auto-scaling adjusts cluster size based on demand.
Implement auto-termination
Clusters that sit idle waste money. Set them to terminate after 30 minutes of inactivity.
Use cluster pools
If you’re constantly starting and stopping clusters, pools pre-provision instances that can spin up in seconds instead of minutes. This reduces both waiting time and costs.
Monitor with cost management tools
Databricks provides usage dashboards. Review them regularly and identify wasteful patterns.
I’ve seen companies cut their Databricks costs in half just by implementing these basic practices. The platform is powerful, but that power costs money if you’re not deliberate about resource management.
Real-World Use Cases
Let’s get practical. When should you actually consider Databricks?
You’re doing data science at scale
If your data science team is struggling with model management, experiment tracking, and deployment, Databricks plus MLflow solves those problems elegantly.
You have streaming data needs
Processing real-time event streams alongside historical batch data is Databricks’ sweet spot. The unified approach eliminates the complexity of maintaining separate systems.
You’re building a modern data platform
Migrating from legacy data warehouses or stitching together multiple tools? The lakehouse architecture can consolidate your infrastructure.
You need collaborative analytics
When data engineers, data scientists, and analysts need to work together on the same datasets, Databricks provides that shared workspace.
You’re processing petabytes
If your data volumes are measured in petabytes and traditional databases are choking, Spark-based processing on Databricks scales beautifully.
Where Databricks might not make sense: small datasets (under a few hundred GB), simple reporting needs that a traditional database handles fine, or budgets that can’t accommodate the cost.
Integration with the Ecosystem
One of Databricks’ strengths is that it doesn’t try to be everything. Instead, it integrates with the tools you’re already using.
Data sources
Native connectors for AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage, JDBC databases, Kafka, Kinesis, and dozens more. Getting data in and out is straightforward.
BI tools
Tableau, Power BI, Looker, they all connect to Databricks SQL warehouses using standard JDBC/ODBC drivers.
Orchestration
Airflow, Prefect, and Azure Data Factory can trigger Databricks jobs as part of larger workflows.
Version control
Integrate notebooks with Git (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) for proper version control and CI/CD pipelines.
Monitoring
Send logs and metrics to Datadog, Splunk, or your monitoring tool of choice.
This flexibility means Databricks slots into your existing tech stack rather than forcing you to rebuild everything around it.
Security and Compliance
Look, security isn’t sexy. But it’s non-negotiable, especially when you’re dealing with sensitive data.
Databricks takes security seriously across multiple dimensions:
Network isolation
Use VPC peering or Private Link to ensure data never traverses the public internet. Your Databricks control plane and data plane communicate through private network connections.
Encryption
Data at rest and in transit is encrypted by default. You control the keys through your cloud provider’s key management service.
Identity and access
Integration with Azure Active Directory, AWS IAM, Okta, and other identity providers means you can use your existing authentication systems.
Compliance certifications
Databricks maintains SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and various other compliance certifications. They publish their security whitepaper publicly, worth a read if you’re in a regulated industry.
Data residency
Since the data plane runs in your cloud account, you control where data physically resides. This matters for GDPR and other data sovereignty regulations.
The shared responsibility model applies here. Databricks secures the platform; you’re responsible for properly configuring access controls and following best practices.
Advanced Features
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, Databricks has some advanced capabilities worth exploring:
Delta Sharing
Share live data with external organizations without copying it or losing control. You define what they can access, and they query it directly through open protocols.
Databricks SQL Serverless
SQL warehouses that auto-scale from zero to handle any workload, with sub-second startup times. You only pay for actual query execution.
Repos
Full Git integration for notebooks and code. Proper branching, pull requests, and code review workflows for your data projects.
Feature Store
Centralized repository for ML features with built-in lineage tracking and serving. Define features once, use them everywhere.
Autoloader
Incrementally and efficiently process new data files as they arrive in cloud storage. It automatically infers schemas and handles schema evolution.
These features separate hobbyist usage from enterprise-grade implementations.
Connecting Your Data Stack
Speaking of integrations, and this is particularly relevant if you’re focused on making data accessible across your organization, tools like Livedocs have started bridging the gap between raw data platforms and practical business use.
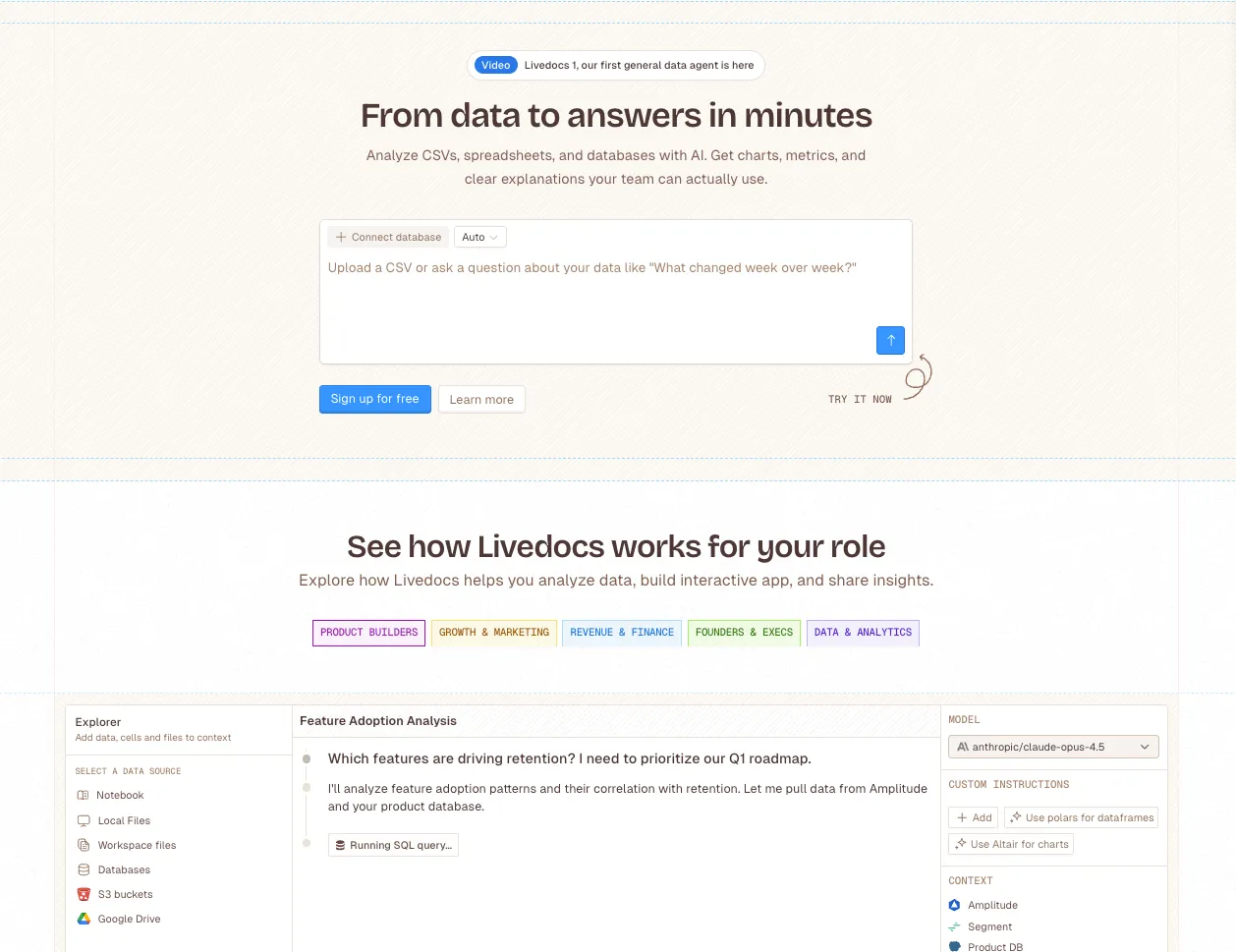
Here’s the situation: Databricks gives you incredible analytical power, but not everyone in your company speaks SQL or Python. You’ve got business users who need insights, and they need them in a format that doesn’t require a computer science degree.
Livedocs has built an interface that connects directly to Databricks, which solves a real problem. Instead of your data team fielding endless ad-hoc requests (“Can you pull Q4 metrics for the Northeast region?” “What were conversion rates last month?” “Show me user cohort trends”), business users can interact with their data through Livedocs’ agent.
The Livedocs agent is particularly strong at data analysis, it can create charts, generate summaries, and answer natural language questions about your data.
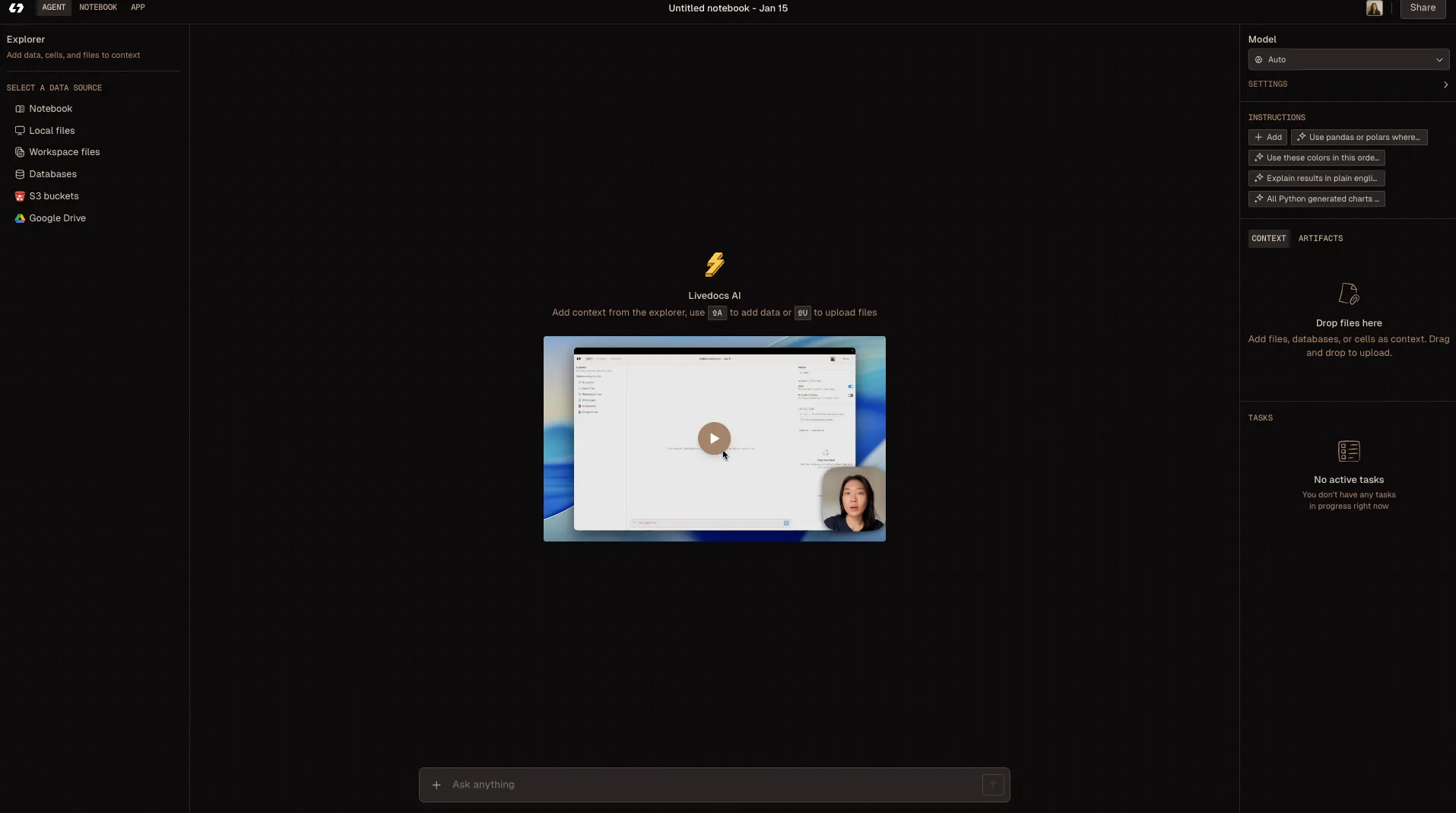
You connect Livedocs to your Databricks instance, and suddenly your marketing team can query campaign performance without submitting a ticket. Your operations team can generate their own reports without waiting three days for the data engineering team to write SQL queries.
What makes this approach compelling is that companies are actually using it in production. The pattern is usually: Databricks for heavy lifting and data transformation, then Livedocs as the presentation layer for business users. Your data stays in Databricks (secure, governed, compliant), but the accessibility dramatically improves.
It’s one of those integrations that makes you think, “Why didn’t we do this sooner?” The technical team maintains control over data quality and security, while business users get the self-service analytics they’ve been asking for.
Databricks for heavy lifting and data transformation, then Livedocs as the presentation layer for business users.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Let me share some mistakes I’ve seen teams make with Databricks, and how to avoid them:
Mistake #1
Over-engineering from day one. You don’t need a perfect medallion architecture with 47 layers of data quality checks on day one. Start simple, prove value, then iterate.
Mistake #2
Ignoring cluster configuration. The default settings are rarely optimal. Spend time understanding your workload and tuning accordingly.
Mistake #3
Not using Delta Lake. I get it, you want to move fast and Delta seems like extra complexity. Trust me, use Delta from the start. The time travel and ACID transactions will save you later.
Mistake #4
Poor naming conventions. Establish clear naming standards for tables, schemas, notebooks, and jobs from day one. Future you will be grateful.
Mistake #5
Treating notebooks like production code. Notebooks are great for exploration and experimentation. For production pipelines, consider modular Python packages with proper testing and CI/CD.
Mistake #6
Neglecting documentation. Document your data models, transformation logic, and business definitions. Your teammates (and future self) need context.
The Future of DatabricksThe platform is evolving rapidly. Recent developments and future directions include:
Deeper AI integration beyond just ML model training. Expect more automated optimization, intelligent query tuning, and AI-assisted data engineering.
Better support for unstructured data, documents, images, audio. As LLMs and vector databases become mainstream, Databricks is positioning to handle these workloads natively.
Continued focus on simplifying the developer experience. The trend is toward higher-level abstractions that let you express intent without worrying about implementation details.
Tighter integration with the broader data ecosystem. More connectors, better compatibility, and standards-based approaches that reduce lock-in.
Final Thoughts
The learning curve is real. Databricks has many moving parts, and mastery takes time. But the investment pays off through increased productivity, better collaboration, and unified data infrastructure.
What I appreciate most about Databricks is that it takes genuinely hard problems, distributed computing, data reliability, model lifecycle management, and makes them manageable. Not trivial, but manageable. That’s a meaningful achievement in an industry that loves complexity for complexity’s sake.
Whether you’re just starting your data journey or looking to modernize existing infrastructure, understanding Databricks gives you a powerful tool for tackling modern data challenges. The platform has its quirks and costs, but the core value proposition is solid: unified analytics that actually works.
Get started with Livedocs and build your first live notebook in minutes.
- 💬 If you have questions or feedback, please email directly at a[at]livedocs[dot]com
- 📣 Take Livedocs for a spin over at livedocs.com/start. Livedocs has a great free plan, with $10 per month of LLM usage on every plan
- 🤝 Say hello to the team on X and LinkedIn
Stay tuned for the next article!
Ready to analyze your data?
Upload your CSV, spreadsheet, or connect to a database. Get charts, metrics, and clear explanations in minutes.
No signup required — start analyzing instantly

